Login form
Solar System
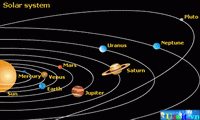
 Solar System, the Sun and everything that orbits the Sun, including the planets and their satellites; the dwarf planets, asteroids, Kuiper Belt Objects, and comets; and interplanetary dust and gas. The term may also refer to a group of celestial bodies orbiting another star (see Extrasolar Planets). In this article, solar system refers to the system that includes Earth and the Sun.
Solar System, the Sun and everything that orbits the Sun, including the planets and their satellites; the dwarf planets, asteroids, Kuiper Belt Objects, and comets; and interplanetary dust and gas. The term may also refer to a group of celestial bodies orbiting another star (see Extrasolar Planets). In this article, solar system refers to the system that includes Earth and the Sun.
The dimensions of the solar system are specified in terms of the mean distance from Earth to the Sun, called the astronomical unit (AU). One AU is 150 million km (about 93 million mi).
Estimates for the boundary where the Sun’s magnetic field ends and interstellar space begins—called the heliopause—range from 86 to 100 AU from the Sun.
 The most distant known body orbiting the Sun is the dwarf planet Eris, whose discovery was reported in July 2005. Eris is currently about 97 AU from the Sun. Another planetlike object in the outer solar system named Sedna is currently at 90 AU but will reach about 900 AU at the farthest point in its orbit thousands of years from now. Comets known as long-period comets, however, achieve the greatest distance from the Sun; they have highly eccentric orbits ranging out to 50,000 AU or more. (A comet’s period is how long it takes it to complete one revolution about the Sun.)
The most distant known body orbiting the Sun is the dwarf planet Eris, whose discovery was reported in July 2005. Eris is currently about 97 AU from the Sun. Another planetlike object in the outer solar system named Sedna is currently at 90 AU but will reach about 900 AU at the farthest point in its orbit thousands of years from now. Comets known as long-period comets, however, achieve the greatest distance from the Sun; they have highly eccentric orbits ranging out to 50,000 AU or more. (A comet’s period is how long it takes it to complete one revolution about the Sun.)
They are members of the Oort cloud, a spherical shell of comet nuclei that surrounds the flat plane of planetary orbits at this enormous distance.

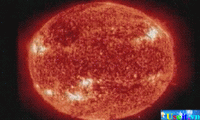 Sun
Sun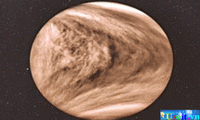 Venus is the brightest object in our sky, after the sun and moon. Swirling clouds of sulfur and sulfuric acid obscure Venus’s surface and inhibited study of the planet from Earth until technology permitted space vehicles, outfitted with probes, to visit it. These probes determined that Venus is the hottest of the planets, with a surface temperature of about 460° C (about 860° F). Scientists believe that a greenhouse effect causes the extreme temperature, hypothesizing that the planet’s thick clouds and dense atmosphere trap energy from the sun.
Venus is the brightest object in our sky, after the sun and moon. Swirling clouds of sulfur and sulfuric acid obscure Venus’s surface and inhibited study of the planet from Earth until technology permitted space vehicles, outfitted with probes, to visit it. These probes determined that Venus is the hottest of the planets, with a surface temperature of about 460° C (about 860° F). Scientists believe that a greenhouse effect causes the extreme temperature, hypothesizing that the planet’s thick clouds and dense atmosphere trap energy from the sun.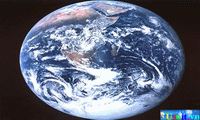 An oxygen-rich and protective atmosphere, moderate temperatures, abundant water, and a varied chemical composition enable Earth to support life, the only planet known to harbor life. The planet is composed of rock and metal, which are present in molten form beneath its surface. The Apollo 17 spacecraft took this snapshot in 1972 of the
An oxygen-rich and protective atmosphere, moderate temperatures, abundant water, and a varied chemical composition enable Earth to support life, the only planet known to harbor life. The planet is composed of rock and metal, which are present in molten form beneath its surface. The Apollo 17 spacecraft took this snapshot in 1972 of the 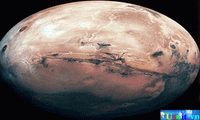 The most detailed information available about Mars has come from unpiloted spacecraft sent to the planet by the
The most detailed information available about Mars has come from unpiloted spacecraft sent to the planet by the  Jupiter is the largest of the planets, with a volume more than 1,300 times greater than that of Earth. Jupiter’s colorful bands are caused by strong atmospheric currents and accentuated by a dense cloud cover. The massive planet, upper right, is shown here with its four largest satellites: Io, upper left, Ganymede, lower left, Europa, center, and Callisto, lower right
Jupiter is the largest of the planets, with a volume more than 1,300 times greater than that of Earth. Jupiter’s colorful bands are caused by strong atmospheric currents and accentuated by a dense cloud cover. The massive planet, upper right, is shown here with its four largest satellites: Io, upper left, Ganymede, lower left, Europa, center, and Callisto, lower right Saturn, distinguished by its rings, is the second largest planet in the solar system. This processed Hubble Space Telescope image shows the planet’s cloud bands, storms, and rings as they would appear to the human eye.
Saturn, distinguished by its rings, is the second largest planet in the solar system. This processed Hubble Space Telescope image shows the planet’s cloud bands, storms, and rings as they would appear to the human eye.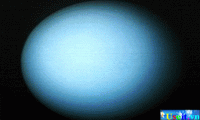 Uranus’s blue-green color comes from the methane gas present in its cold, clear atmosphere. The dark shadings at the right edge of the sphere correspond to the day-night boundary on the planet. Beyond this boundary, Uranus’s northern hemisphere remains in a four-decade-long period of darkness because of the way the planet rotates. Scientists compiled this view of Uranus from images returned from Voyager 2 in 1986, when the probe was 9.1 million km (5.7 million mi) away from the planet.
Uranus’s blue-green color comes from the methane gas present in its cold, clear atmosphere. The dark shadings at the right edge of the sphere correspond to the day-night boundary on the planet. Beyond this boundary, Uranus’s northern hemisphere remains in a four-decade-long period of darkness because of the way the planet rotates. Scientists compiled this view of Uranus from images returned from Voyager 2 in 1986, when the probe was 9.1 million km (5.7 million mi) away from the planet. This image of
This image of  Pluto is farther from the Sun than the major planets in the solar system, although it occasionally moves in closer than
Pluto is farther from the Sun than the major planets in the solar system, although it occasionally moves in closer than 